Authorization Process
What is this process used for?
The authorization process was designed to give application providers of applications the chance to make sure, they know, which account is assigned to which agrirouter account. Otherwise, fake accounts could consume data on their costs.
|
As the authorization process – in difference to the rest of the communication – provides a request to your agrirouter integration and not the response to a request from your agrirouter integration, the documentation of the parameters is done in a little different way and there is no description for a HTTP Response code, because we don’t get one. |
The authorization process is required for farming software and telemetry platforms, for CUs it is an optional function.
For CUs, this requires additional infrastructure, therefore DKE advises to use the registration code exchange process.
Authorization of farming software
The application provider should make sure that only such agrirouter accounts can onboard one of his applications that he can assign to one of his users.
|
As the user has to log on to agrirouter, the authorization process requires a browser UI! |
Preparation
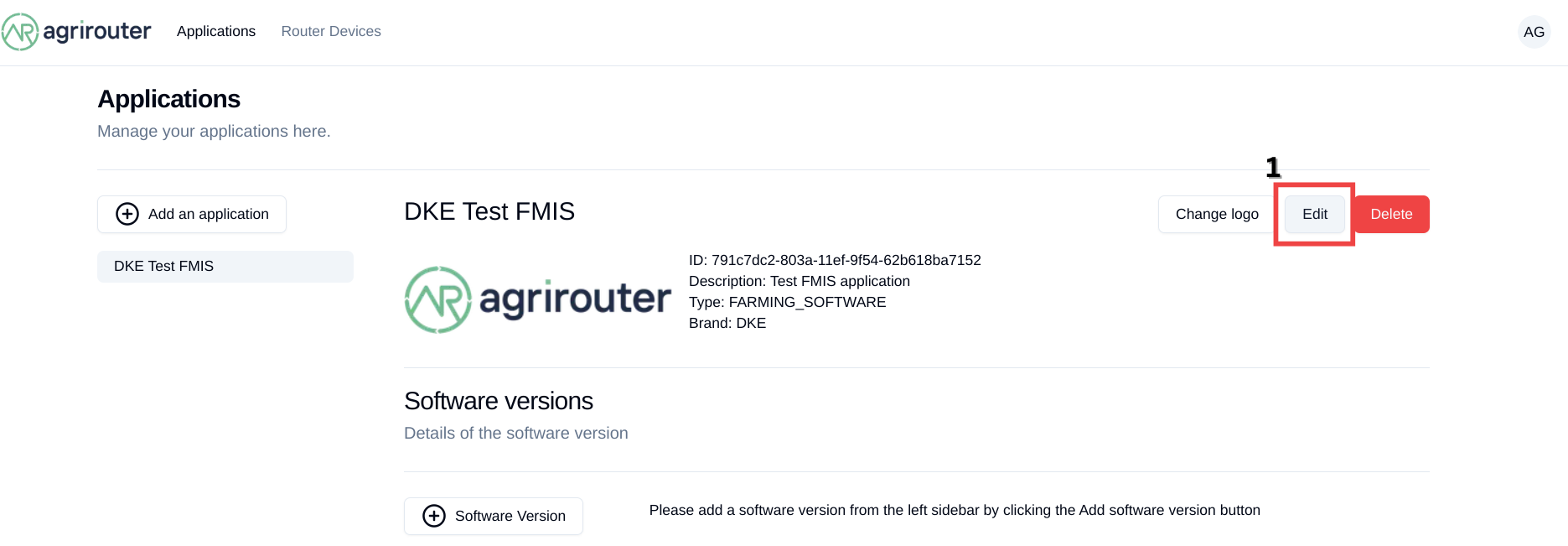
To provide authorization, the developer first has to setup the application.
In the developers' UI, he has to:
-
Copy the application ID (1)
-
Call Edit (2)
-
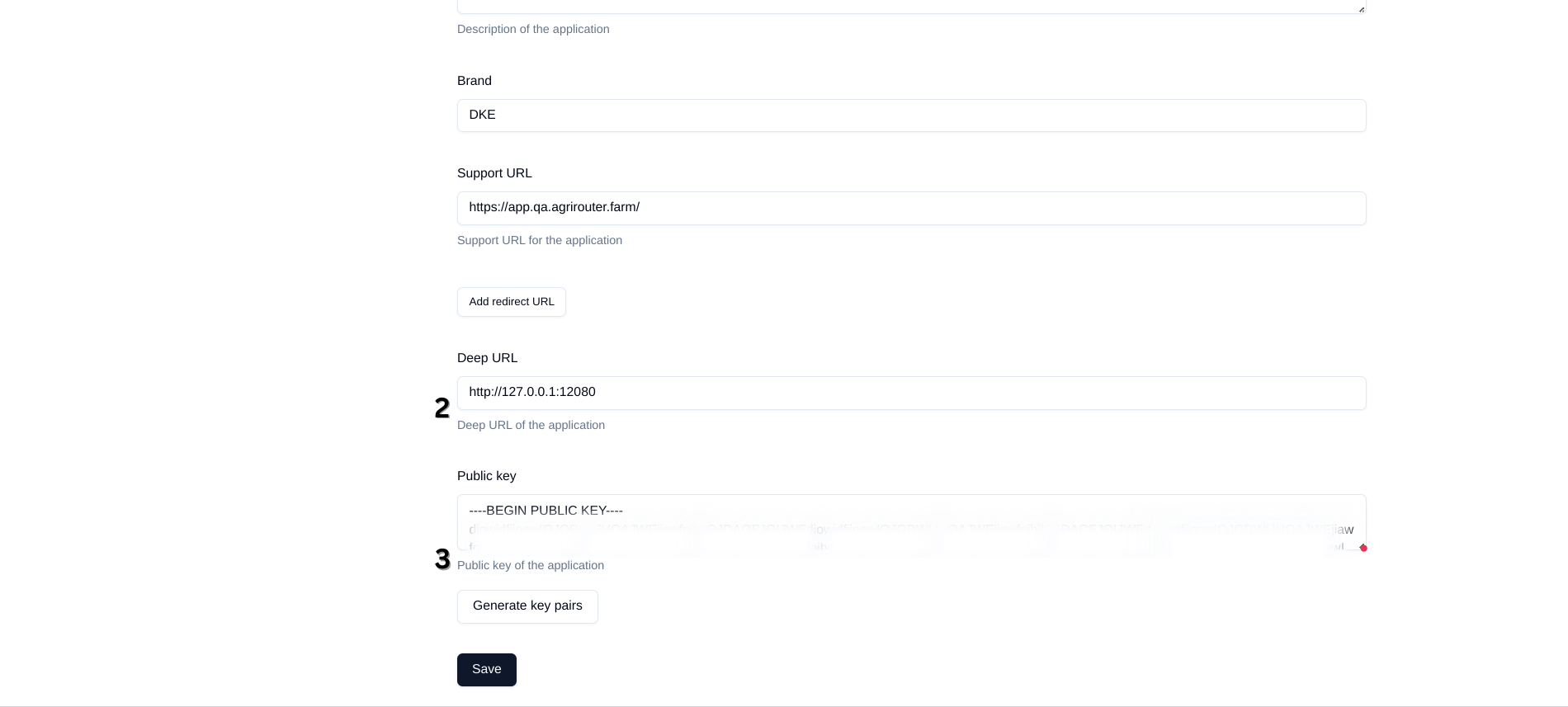
Provide one or more redirect URLs, to which agrirouter shall deliver the authorization result using HTTP 301 Browser redirect.(3)
-
Provide a public key for his encryption or create a key pair on the agrirouter frontend
|
During development, if your application is not yet reachable publicly or you are developing for a desktop application, you can just use http://127.0.0.1, plus any port number (e.g. http://127.0.0.1:12080). |
Authorization Process Overview
The authentication process works as follows:
To better understand what happens here, try the following:
-
Call https://httpbin.org/get in your browser. You’ll get a JSON view of the get request
-
Call https://httpbin.org/get?Param1=Value1&Param2=Value2 in your browser. You’ll get a view of the get request
-
https://httpbin.org simply echoes the request that is sent to the page. That’s important to understand
-
|
Generating an authorization URL
The base URL can be found here.
The authorization Link is a HTTP GET Request that has to be called from a browser.
| Method | Address |
|---|---|
GET |
/application/{{applicationID}}/authorize |
To provide a link for authorization, create a link like this:
{{agrirouter-url}}/application/{{applicationID}}/authorize?{{response_type}}&{{state}}&{{redirect_uri}}
| Parameter | Example Value | Remark |
|---|---|---|
{{agrirouter-url}} |
see above |
Differentiates between QA and Live system |
{{applicationID}} |
Noted from the agrirouter UI |
|
{{response_type}} |
response_type=onboard |
Possible values: verify: only verify the user, onboard: verify user and create a Registration Code (Token) |
{{state}} |
state=w4st556dr543d4wr4s4 |
A number to identify the request result on server side. The provided Number should be:
|
{{redirect_uri}} |
Could extend one of your entered redirect URLs. The base redirect URLs need to be configured by the application developer in the UI. If this query parameter is omitted, the first configured URL will be used. This parameter can override the configured URL as long as one configured URL is a substring of the one defined in the request (e.g. configured: example.com/callback |
|
Calling this link will deliver a website to log in to agrirouter, therefore, this link has to be called through a browser! |
|
The response type onboard can be used to onboard farming applications without having to create a Registration Code in the agrirouter UI. |
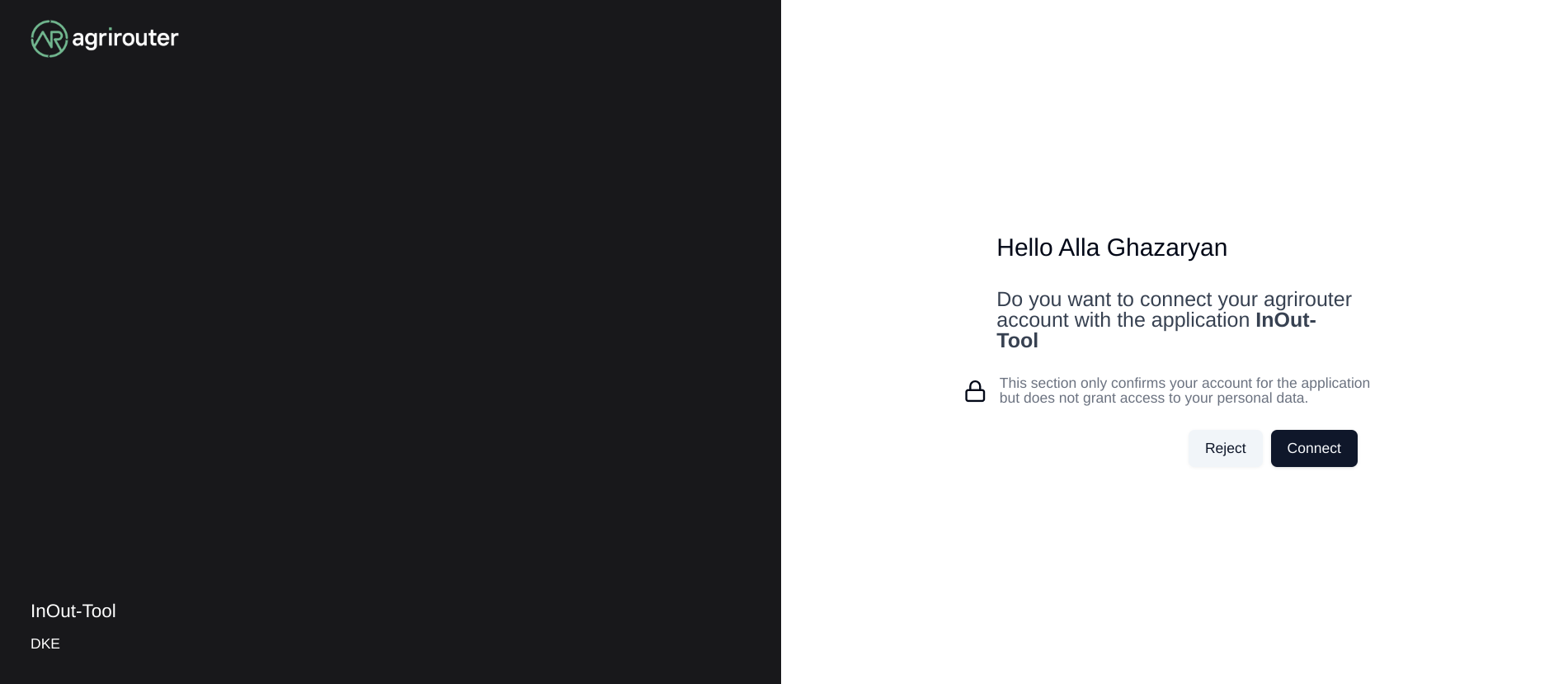
Perform authorization
When the user clicks on the link, the agrirouter website is called. If the user is currently not logged in, he has to log in. After logging in, he is delivered a website to authorize the connection between agrirouter and the application provider:
Analyse result
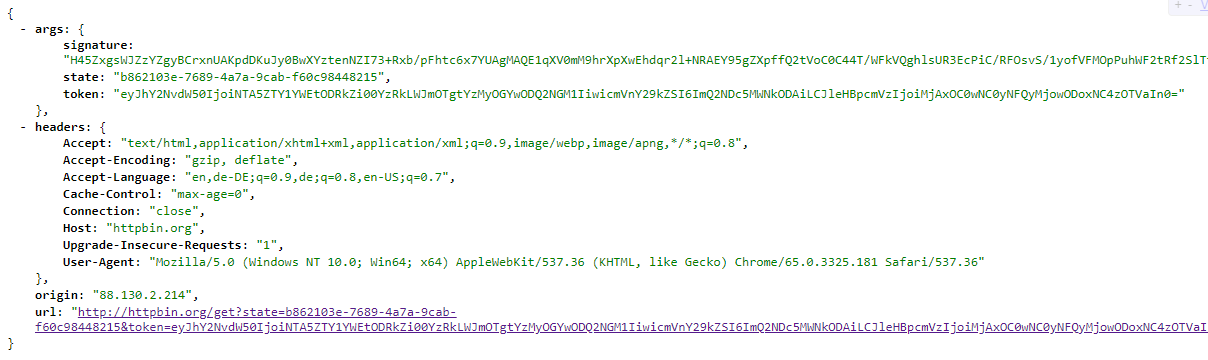
agrirouter sends an HTTP 301 redirect to the browser, encoding the authorization result in a GET queue attached to the Redirect URL entered in the developers' application settings.
The browser reacts in requesting this redirect URL which performs a GET request at the endpoint of the address. The first redirect URL set comes into play when an authorize request does not provide a redirect URL (or provides an invalid one). Please note that this behaviour is DEPRECIATED and we will require a VALID redirect URL to be provided to an Authorise request in the future.
The following parameters will be delivered in the GET-Query:
| Position | Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
signature |
String |
A base64 encoded signature to verify that the source of the message is the agrirouter |
2 |
state |
String |
The value that was passed to the agrirouter in parameter State |
3 |
token |
String |
A base64 encoded JSON Object as Result |
(3) |
error |
String |
If error is delivered, user declined connection! |
Checking for errors
If the result includes a parameter error, the request was declined. Possible values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
request_declined |
The user clicked on "decline" |
Checking authenticity
Before analyzing the result, which is encoded in the token, it should be made sure that the result (provided to the browser and from there to the application provider’s server) is really provided by the agrirouter.
Steps:
-
concatenate
stateandtokenfrom the query -
create the SHA256 hash of the concatenated string
-
verify the authenticity of the
signaturewith the agrirouter public key and generated hash
|
Make sure you do not use the public key you got when you created your application in agrirouter! You have to use the key from Certificates and keys! |
|
Analyse the result in token
The result token is a base64 encoded JSON object including the following parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
account |
String |
The unique id of the user account on agrirouter that will be provided to you in the metrics exports for billing |
regcode |
String |
If |
expires |
DataTime |
The date and time (in UTC) when the regcode becomes invalid |
| The account ID is used for invoicing. Therefore it should be saved with the onboarding reponse together, so the check of the invoice is possible. If the account ID is missing comparing the items on the invoice is not possible, since the invoicing is based on the account ID. |
EXAMPLE
{
"account": "31c83d5d-c307-42f9-80b1-6fc9324823b8",
"regcode": "f75bfbd41b",
"expires": "2018-02-27T10:49:04.901Z"
}Authorization for CUs and non-cloud-software
To perform authorization for software that is not provided as a cloud solution, a small cloud onboarding service could be created to handle the onboarding communication:
|
Make sure, you save all the information returned from the authorization request, as you will e.g. need the account id for the Revoke functionality! |